Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (3): 329-334.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.03.001
Allogenic versus autologous bone filled cages for cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Sun Jia-jia, Yang Hui-lin, Zhou Jun, Zhang Bin, Zhang Kai
- First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2015-01-15Published:2015-01-15 -
Contact:Yang Hui-lin, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Sun Jia-jia, Studying for master’s degree, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:a grant from the Clinical Research Center of Jiangsu Province, No. BL2012004
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Jia-jia, Yang Hui-lin, Zhou Jun, Zhang Bin, Zhang Kai. Allogenic versus autologous bone filled cages for cervical spondylotic myelopathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(3): 329-334.
share this article
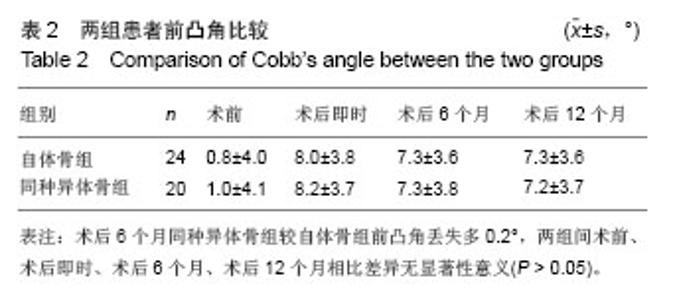
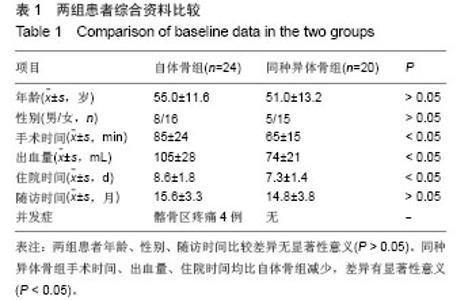
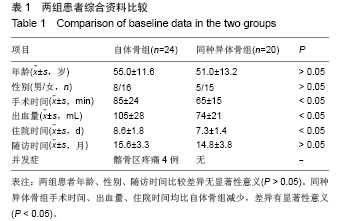
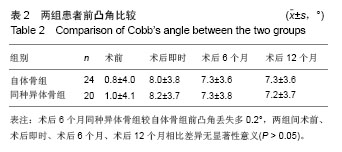
2.3 临床修复效果 自体骨组术前JOA评分为6-11分,平均8.5分;术后JOA 评分11-17分,平均14.8分,术后比术前明显提高(P < 0.05),JOA改善率为优(83%)。同种异体骨组术前JOA评分7-12分,平均8.8分;术后JOA评分11-17分,平均15.0 分,术后比术前明显提高(P < 0.05),JOA改善率为优(84%)。同种异体骨组JOA改善率与自体骨组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 自体骨组术后临床疗效评定(Odom’s标准):优18例,良4例,中2例,优良率为92%。同种异体骨组术后临床疗效(Odom’s标准):优17例,良3例,优良率为100%。同种异体骨组优良率高于自体骨组。 2.4 影像学观察 自体骨组术后3个月20例20节段融合,融合率为83%;术后6个月全部融合。同种异体骨组术后3个月10例10节段融合,融合率为50%;术后 6个月18例18节段融合,融合率90%;术后12个月全部融合。 两组间前凸角变化见表2,同种异体骨组术后6个月前凸角丢失较自体骨组多0.2°,术后6,12个月时两组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。"
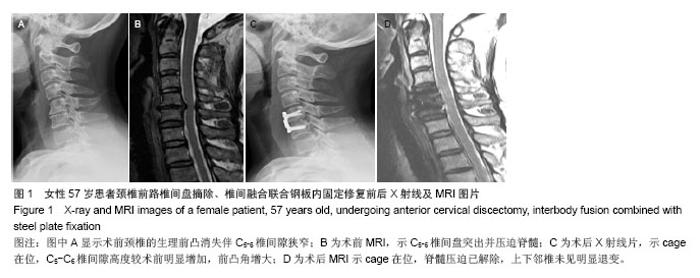
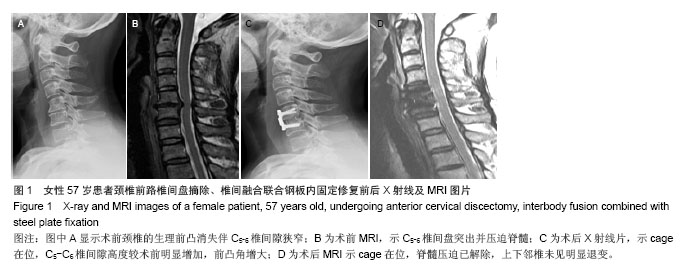
2.5 典型病例 女性患者,57岁,颈肩痛伴双手麻木无力14个月,加重1个月。 X射线片示颈椎反弓,C5-C6椎间隙狭窄明显,见图1A;MR示C5-C6椎间盘突出压迫脊髓,见图1B。术前JOA评分10分,术前前凸角-1.5°。 患者于本院行颈椎前路椎间盘摘除、椎间融合联合钢板内固定,手术时间75 min,术中出血60 mL,手术顺利,术后住院5 d。 随访14个月,无慢性发热、感染等并发症。术后X射线片示cage在位,C5-C6椎间隙高度较术前明显增加,前凸角增大,见图1C;MRI示cage在位,脊髓压迫已解除,上下邻椎未见明显退变,见图1D。术后12个月复查X射线片,恢复良好。术后1年双手无力症状明显改善,伴有轻度麻木,JOA评分16分,前凸角5.5°。 2.6 不良事件 本试验所有入组患者术中均未出现严重并发症,如损伤脊髓、神经、椎动脉、食管、气管等重要器官,术后颈部手术切口及供骨区切口均愈合良好,术后1年随访显示,44例患者中无钢板、螺钉松动,椎间融合器在位。 同种异体骨填充组中有2例患者术后个6月随访时仍未形成完全骨性融合,嘱其减少颈部活动,另外自体骨移植组取骨区患者感存在慢性疼痛症状者4例。"
| [1]Lin Q, Zhou X, Wang X, et al. A comparison of anterior cervical discectomy and corpectomy in patients with multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(3): 474-481. [2]Woods BI, Hohl J, Lee J, et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3):688-695. [3]Zimmermann G, Moghaddam A. Allograft bone matrix versus synthetic bone graft substitutes. Injury. 2011;42:S16-S21. [4]Parish A, Hing K, Davis G. Quantifying structural quality of bone regeneration within a porous bone graft substitute. Bone Joint J Orthop Proc Suppl. 2014;96(Supp 11):319. [5]Lad SP, Nathan JK, Boakye M. Trends in the use of bone morphogenetic protein as a substitute to autologous iliac crest bone grafting for spinal fusion procedures in the United States. Spine. 2011;36(4): E274-281. [6]Skeppholm M, Olerud C. Pain from donor site after anterior cervical fusion with bone graft: a prospective randomized study with 12 months of follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(1): 142-147. [7]Landriel FA, Hem S, Goldschmidt E, et al. Polyetheretherketone interbody cages versus autogenous iliac crest bone grafts with anterior fixation for cervical disc disease. J Spinal Dis Tech. 2013;26(2):61-67. [8]Faldini C, Miscione MT, Acri F, et al. Single level cervical fusion by an anterior approach using autologous bone graft influences the adjacent levels degenerative changes: clinical and radiographic results at 10-year minimum follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(1):90-93. [9]高顺红.同种异体骨移植的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,19(21):1797-1799. [10]左健,康建敏,潘乐.同种异体骨移植用于骨缺损修复的应用现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(18):3395-3398. [11]Froum SJ, Wallace S, Cho SC, et al. Histomorphometric Comparison of Different Concentrations of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein with Allogeneic Bone Compared to the Use of 100% Mineralized Cancellous Bone Allograft in Maxillary Sinus Grafting. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2012;33(6):721-730. [12]Fretwurst T, Spanou A, Nelson K, et al. Comparison of four different allogeneic bone grafts for alveolar ridge reconstruction: a preliminary histologic and biochemical analysis. Oral Surg. 2014;118(4):424-431. [13]Kang J, An H, Hilibrand A, et al. Grafton and local bone have comparable outcomes to iliac crest bone in instrumented single-level lumbar fusions. Spine. 2012; 37(12):1083-1091. [14]Faldini C, Chehrassan M, Miscione MT, et al. Single-level anterior cervical discectomy and interbody fusion using PEEK anatomical cervical cage and allograft bone. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(4):201-205. [15]刘艺,李钦亮,陈鸣,等.同种异体骨在脊髓型颈椎病后路双开门椎管扩大植骨成形术中的应用[J].江苏医药,2010,36(16):1875-1877. [16]施建党,王自立,王沛,等.同种异体骨与自体骨在颈椎结核植骨融合中的应用比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011,25(11): 1290-1293. [17]李翔,戴志唐,常新,等.颈椎前路手术对脊髓型颈椎病患者椎间盘组织中炎性细胞因子的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2011, 28(11): 1988-1990. [18]李云鹏,陈晓亮,马进峰,等.应用同种异体植骨融合术治疗脊髓型颈椎病的远期疗效[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2013,34(3):205-209. [19]陈同磊,成茂华,沈忆新,等.自体骨或硫酸钙人工骨结合 MC+® 椎间融合器在颈椎前路融合中的应用:疗效及并发症比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2010,14(4):718-721. [20]Epstein NE. Iliac crest autograft versus alternative constructs for anterior cervical spine surgery: Pros, cons, and costs. Surg Neurol Int. 2012;3(Suppl 3):S143. [21]Smith GW, Robinson RA. The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg. 1958;40(3):607-624. [22]Cloward RB. The anterior approach for removal of ruptured cervical disks. J Neurosurg. 1958;15(6):602-617. [23]Hinsenkamp M, Muylle L, Eastlund T, et al. Adverse reactions and events related to musculoskeletal allografts: reviewed by the World Health Organisation Project NOTIFY. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(3):633-641. [24]Kang J, An H, Hilibrand A, et al. Grafton and local bone have comparable outcomes to iliac crest bone in instrumented single-level lumbar fusions. Spine. 2012;37(12):1083-1091. [25]Kumaresan S, Yoganandan N, Pintar F A, et al. Contribution of disc degeneration to osteophyte formation in the cervical spine: a biomechanical investigation. J Orthop Res. 2001; 19(5):977-984. [26]Lee FY, Hazan EJ, Gebhardt MC, et al. Experimental model for allograft incorporation and allograft fracture repair. J Orthop Res. 2000;18(2):303-306. [27]黄长明,王臻.大段同种异体骨移植愈合的实验研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2000,15(5):355-358. [28]Lamb KE, Lodhi S, Meier-Kriesche HU. Long‐Term Renal Allograft Survival in the United States: A Critical Reappraisal. Am J Trans. 2011;11(3):450-462. [29]Wood RA, Mealey BL. Histologic comparison of healing after tooth extraction with ridge preservation using mineralized versus demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft. J Periodontol. 2012;83(3):329-336. [30]Miller LE, Block JE. Safety and effectiveness of bone allografts in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion surgery. Spine. 2011; 36(24): 2045-2050. [31]Macdonald RL, Fehlings MG, Tator CH, et al. Multilevel anterior cervical corpectomy and fibular allograft fusion for cervical myelopathy. J Neurosurg. 1997;86(6):990-997. [32]Yue WM, Brodner W, Highland TR. Long-term results after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with allograft and plating: a 5-to 11-year radiologic and clinical follow-up study. Spine. 2005; 30(19):2138-2144. [33]Rintala DH, Loubser PG, Castro J, et al. Chronic pain in a community-based sample of men with spinal cord injury: prevalence, severity, and relationship with impairment, disability, handicap, and subjective well-being. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(6):604-614. [34]Hawker GA, Gignac MAM, Badley E, et al. A longitudinal study to explain the pain‐depression link in older adults with osteoarthritis. Arth Care Res. 2011;63(10):1382-1390. [35]Rudy TE, Kerns RD, Turk DC. Chronic pain and depression: toward a cognitive-behavioral mediation model. Pain. 1988; 35(2):129-140. [36]Latimer AE, Ginis KA, Hicks AL, et al. An examination of the mechanisms of exercise-induced change in psychological well-being among people with spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2004;41(5):643-652. [37]Dagci T, Armagan G, Konyalioglu S,et al. Alterations in the expression of the apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease-1/redox factor-1 (APE/ref-1) and DNA damage in the caudal region of acute and chronic spinal cord injured rats treated by embryonic neural stem cells. Phys Res. 2009;58(3):427-434. [38]陈德强,张鹏.骨髓复合人工骨治疗骨折不愈合的临床观察[J]. 中国误诊学杂志, 2007,7(16):3741-3742. [39]Bahney CS, Hu DP, Taylor AJ, et al. Stem Cell–Derived Endochondral Cartilage Stimulates Bone Healing by Tissue Transformation. J Bone Mineral Res. 2014;29(5):1269-1282. [40]Behr B, Sorkin M, Lehnhardt M, et al. A comparative analysis of the osteogenic effects of BMP-2, FGF-2, and VEGFA in a calvarial defect model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(9-10): 1079-1086. |
| [1] | Tang Xiaokai, Li Weiming. Role and mechanism of Nel-like molecule-1 in promoting bone fusion after spinal fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3914-3920. |
| [2] | Chen Jiang, Li Jinyu, Zheng Chenying, Bai Chunxiao, Zhang Fan, Liu Chuyin, Zhao Xueqian, Yuan Qiaomei, Di Xueshi, Kang Shengqian, Jia Yusong . Changes in sagittal parameters of cervical spine after double-segment artificial cervical disc replacement and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2341-2346. |
| [3] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [4] | Cao Liangliang, Xu Jianguang, Mei Wei. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the biomechanical changes of the lumbar spine after the combination of intervertebral fusion with dynamic internal fixation of the interspinous process in the lumbosacral region [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1905-1910. |
| [5] | Fu Jiaxin, Xiao Lianping, Wang Shusen, Li Xiaodong, Han Liqiang, Wang Tonghao. Therapeutic effects of paraspinal approach combined with internal fixation through pedicle of fractured vertebra versus traditional AF screw-rod system for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1177-1181. |
| [6] | Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan. Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1188-1195. |
| [7] | Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang . Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1196-1202. |
| [8] | Wang Liang, Li Lijun, Zhu Fuliang, Jiang Zhuyan, Wang Shuai, Ni Dongkui . Cortical bone trajectory screw versus pedicle screw fixation after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1291-1298. |
| [9] | Liang Long, Wei Xu, Zhu Liguo, Yin He, Yu Jie, Feng Minshan, Chen Lin. Cervical posterior single-door laminoplasty versus double-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1299-1306. |
| [10] | Fan Zhirong, Peng Jiajie, Zhong Degui, Zhou Lin, Su Haitao, Huang Yongquan, Wu Jianglin, Liang Yihao. Suture anchor combined with open reduction and internal fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for ankle fracture combined with deltoid ligament injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1307-1312. |
| [11] | Zhou Yu, Liu Yuehong, Liu Shuping, Chen Xi, Qin Wei, Li Qifeng. Spinal stability of intervertebral grafting reinforced by five or six augmenting screws versus transvertebral grafting reinforced by four augmenting screws for thoracolumbar vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 505-511. |
| [12] | Li Qingsong, Liu Shaoyu, Yin Zongsheng. Multiple posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion instrumentation for thoracolumbar kyphosis and osteoporotic fracture in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 512-517. |
| [13] | Li Xianzhou, Wang Qian, Zhang Cunxin . Lumbar spondylolisthesis: status and prospects of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 621-627. |
| [14] | Yin Hao, Zhou Enchang, Pan Zhengjun, Chen Guang, Jiang Hua. Finite element analysis of the four and three cannulated screws combined with buttress plate fixation for the treatment of Pauwels III femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5133-5137. |
| [15] | Yi Guoliang, Wang Shankun, Song Xizheng. Biomechanical testing of the locking axial lumbosacral interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4546-4551. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||